general health
normal behaviour in a field or stable
unnormal behaviour in field or stable
- bucking
- rolling
- standing in the shade when its hot
- grooming their mate
- alert
- lied down
- eating food
unnormal behaviour in field or stable
- kicking
- bitting
- pawing
- trying to jump the fences
- neighing costantly
- galloping around theperimetere of the feild
- lamness
- dull coat
- not eating
worming
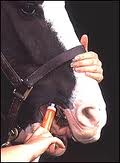
1. tie up your horse and make sure its mouth is empty
2. Insert the syringe into the corner of the horse's mouth at an angle of about 45 degrees to his head, (there are no teeth there).
3. Push the syringe gently into its mouth and push the plunger so that the wormer goes into the horse’s mouth
4. Wiggle the syringe around the mouth to get rid of any excess wormer
5. Lift the horse's head as you depress the plunger to encourage the horse to swallow the paste and keep his head up until he has swallowed the paste.
6. Make sure the syringe is empty and that the correct amount has been given
It is critical that the horse is wormed at the correct dose for his weight and height. Under treatment can lead to the worms becoming immune to a particular brand of treatment, thus producing a 'super worm.”
Equine Annual Worming Schedule
January to March routine worming
April Tapeworm
May to September Routine Worming
October Tapeworm
November Encysted Red worm
December Bot Worming.er-worm.”
You should worm your horse every 6-8 weeks .
teeth
Dental care is as important to horses as it
is to humans. Making sure their teeth are healthy therefore sees if they are
getting value from there food and you can see how well they will perform.
Horses have 36-40 teeth. Adult horses have six front teeth (incisors) and twelve molars.
Male horses also have four tushes at one each side of both jaws. Females may
have them but they are much smaller. Horse’s teeth never stop growing. Grazing
allows their teeth to be worn down. All teeth are normally erupted by the age of
five, at which point the horse is said to have a "full mouth", but the actual
age this occurs will depend on the individual horse, and also by breed, with
certain breeds having different average eruption times. For instance, in
Shetland ponies the middle and corner incisor tend to erupt late, and in draft
horses and miniature horses, the permanent middle and corner incisors are usual
late appearing.Horses can get all sort of dental problems. The wear of the teeth can cause problems if
it is uneven, with sharp points appearing, especially on the outer edge of the
molars, the inner edge of the premolars and the posterior end of the last molars
on the bottom jaw. Other common problems include abscessed, loose, infected,
crack teeth, retained deciduous teeth and plague build up.
Wolf teeth can also cause problems.To prevent teeth problems it is
recommended to have a vet cheek their teeth every 6 months. Certain individuals
need to have their teeth cheeked more often. Many horses need floating. This
process that involves a veterinarian wearing down the surface of the teeth,
usually to remove sharp points or to balance out the mouth. However they must be
careful that they do not take too much off. If they do it can prevent them from
eating.
is to humans. Making sure their teeth are healthy therefore sees if they are
getting value from there food and you can see how well they will perform.
Horses have 36-40 teeth. Adult horses have six front teeth (incisors) and twelve molars.
Male horses also have four tushes at one each side of both jaws. Females may
have them but they are much smaller. Horse’s teeth never stop growing. Grazing
allows their teeth to be worn down. All teeth are normally erupted by the age of
five, at which point the horse is said to have a "full mouth", but the actual
age this occurs will depend on the individual horse, and also by breed, with
certain breeds having different average eruption times. For instance, in
Shetland ponies the middle and corner incisor tend to erupt late, and in draft
horses and miniature horses, the permanent middle and corner incisors are usual
late appearing.Horses can get all sort of dental problems. The wear of the teeth can cause problems if
it is uneven, with sharp points appearing, especially on the outer edge of the
molars, the inner edge of the premolars and the posterior end of the last molars
on the bottom jaw. Other common problems include abscessed, loose, infected,
crack teeth, retained deciduous teeth and plague build up.
Wolf teeth can also cause problems.To prevent teeth problems it is
recommended to have a vet cheek their teeth every 6 months. Certain individuals
need to have their teeth cheeked more often. Many horses need floating. This
process that involves a veterinarian wearing down the surface of the teeth,
usually to remove sharp points or to balance out the mouth. However they must be
careful that they do not take too much off. If they do it can prevent them from
eating.
TRP
The normal respiration rate for is 8-20 breaths per minute and a foal has a rate of 20-40 breaths per minute.The average pulse rate for a horse is 28-45 beats per minute and a foal pulse rate varys depending on its age.New born foals have a heart rate between 80-100 beats per minute. Older foals have a heart =rate of 60-80 beats. the normal tempurature of 98.5F. The horses temperature is often higher than the adults.
To take the pulse you place your thumb under the lower jaw or foreleg. To take a horses tempurature yopu put vaseline on th themometer and plac it into the rear.Be careful and approch quietly as they may kick. To take a horses respiration you look at the thorax and evaluate the nostril flare.
To take the pulse you place your thumb under the lower jaw or foreleg. To take a horses tempurature yopu put vaseline on th themometer and plac it into the rear.Be careful and approch quietly as they may kick. To take a horses respiration you look at the thorax and evaluate the nostril flare.
illnesses
colic- colic means any sort of pain in the
stomach area and can range from discomfort to death. Warning signs include
rolling, pawing the ground, looking at the flanks and sweating. The horse may
also not pass droppings.
African horse sickness- AHS (African horse
sickness) is one of the most devastating horse diseases on the planet. It’s
carried by midges but it isn’t contagious so humans and other equines cannot
catch it. At the present day it is contained in Africa but due to climate change
it may spread to England. Signs of
this illness are nasal discharge, excessive salivation and swelling of the eye
or head.
Laminitis-
Is a painful condition in the feet and can affect any animal. There are many
triggers and the most common is an over load of fructans (a type of carbohydrate
in grass and plants). Also other triggers are concussion and stress. Signs of
laminitis are shorter strides, the horse may be reluctant to move and may lie
down and they will keep their weight of their unaffected foot.
Strangles- Strangles is a highly contagious
disease and is often seen in younger horses. The signs of strangles are swelling
below the horse throat ,nasal discharge, raised temperature, loss of appetite,
coughing and general malaise. It is caused by inhaling the bacteria often of
infected horses or clothes.
Ring worm- Ring worm is a fungal infection
in the skin. It is contagious to people as well as other horses. The first stage
appears as tufts of hair coming out of the skin. They will fall out and leave
bald patches.
stomach area and can range from discomfort to death. Warning signs include
rolling, pawing the ground, looking at the flanks and sweating. The horse may
also not pass droppings.
African horse sickness- AHS (African horse
sickness) is one of the most devastating horse diseases on the planet. It’s
carried by midges but it isn’t contagious so humans and other equines cannot
catch it. At the present day it is contained in Africa but due to climate change
it may spread to England. Signs of
this illness are nasal discharge, excessive salivation and swelling of the eye
or head.
Laminitis-
Is a painful condition in the feet and can affect any animal. There are many
triggers and the most common is an over load of fructans (a type of carbohydrate
in grass and plants). Also other triggers are concussion and stress. Signs of
laminitis are shorter strides, the horse may be reluctant to move and may lie
down and they will keep their weight of their unaffected foot.
Strangles- Strangles is a highly contagious
disease and is often seen in younger horses. The signs of strangles are swelling
below the horse throat ,nasal discharge, raised temperature, loss of appetite,
coughing and general malaise. It is caused by inhaling the bacteria often of
infected horses or clothes.
Ring worm- Ring worm is a fungal infection
in the skin. It is contagious to people as well as other horses. The first stage
appears as tufts of hair coming out of the skin. They will fall out and leave
bald patches.
wounds
incisions and laceration
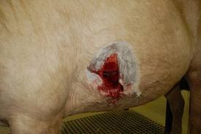
incisions and laceration wounds are often caused by barbed wire or glass.They may bleed alot and be a deep wound.
puncture wounds and penetraiting

penetraiting or puncture are caused mainly by a nail or thorn that they have trodden on. Theese wounds are fairly small but shoukldnt be under estimated.
bruising

contusion wounds are bruisings from kicking from other horses. The damage is under the skin so you can not see it.
abrasions
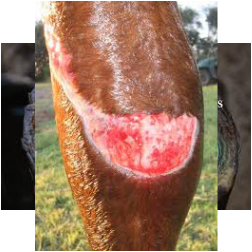
theys wounds are created by friction against a hard surface.It should be cleaned as it may have debris in it.
first aid kit
what you should have in your first aid kit ..........
A card with your vets number
digital theomometer
antiseptic wipes
wound gel
large roll of cotton wool
scissors with curved edges
gamgee(cotton wool sandwiched between layers of of guaze)
poultice
duct tape
dressings - non stick ones to cover wound befor bandageing
bandaging
easy boots
stethoscope
twitch
hoof pick
fly lotion
wire cutters
electrolytes
tourch
A card with your vets number
digital theomometer
antiseptic wipes
wound gel
large roll of cotton wool
scissors with curved edges
gamgee(cotton wool sandwiched between layers of of guaze)
poultice
duct tape
dressings - non stick ones to cover wound befor bandageing
bandaging
easy boots
stethoscope
twitch
hoof pick
fly lotion
wire cutters
electrolytes
tourch


